Technology
Windows Defender: Exploring Its Capabilities as a PC Virus Protection Tool
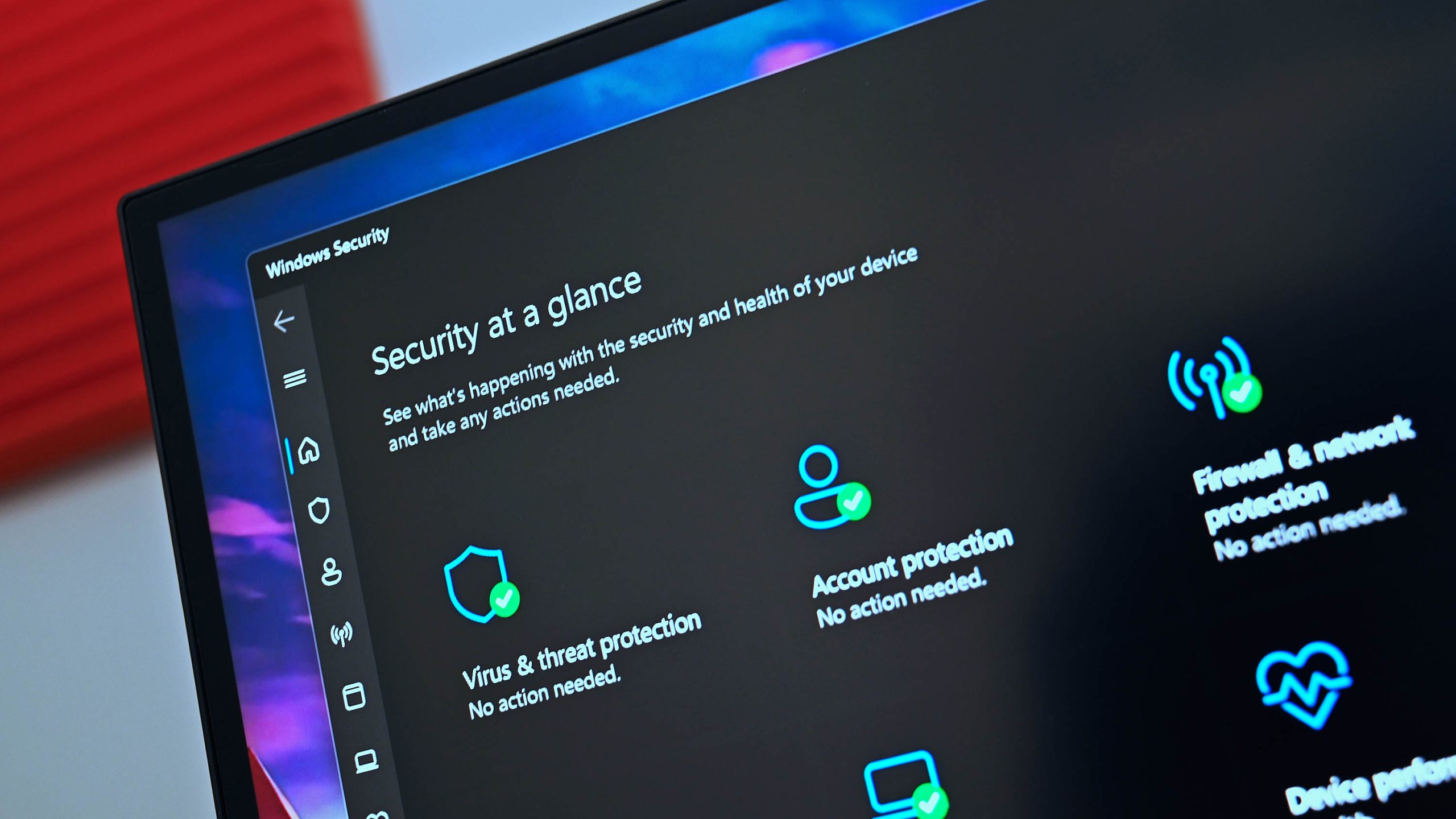
Introduction:
Windows Defender, Microsoft’s built-in antivirus software, has long been a part of the Windows operating system. However, questions regarding its ability to provide sufficient protection against viruses still linger among PC users. In this article, we will delve into the capabilities of Windows Defender and shed light on five essential aspects you should know about its functionality.
- Real-time Protection:
A significant advantage of Windows Defender is its real-time protection feature. By default, this feature runs continuously in the background, scanning files and applications for any signs of threats. As soon as a threat is detected, Windows Defender takes immediate action, either quarantining or removing the malicious software.
- Robust Malware Detection Engine:
Windows Defender employs a powerful malware detection engine, relying on machine learning algorithms. This engine can identify and eliminate various forms of malware, including viruses, Trojan horses, and spyware. Regular database updates, combined with cloud-based protection, enable Windows Defender to swiftly detect and block emerging threats.
- Limited Features:
While it offers essential antivirus protection, it does lack some advanced features found in other antivirus software. For instance, it does not include email scanning, firewall protection, or parental controls. However, users seeking additional functionality can either upgrade to a premium version of another antivirus solution or complement Windows Defender with a third-party tool.
- Keeping Pace with the Latest Threats:
Windows Defender relies on regular updates for its virus definitions. Consequently, there may be a slight lag in detecting the most recent threats. Microsoft continuously works to enhance the software’s virus definitions, but it is worth noting that highly sophisticated viruses may occasionally evade detection.
- A Component of a Comprehensive Security Strategy:
It should be viewed as a fundamental component of a comprehensive security strategy rather than the sole line of defense against viruses and online threats. To maximize protection, it is essential to combine Windows Defender with safe browsing practices, regular software updates, and additional security tools such as firewalls and VPNs.
Conclusion:
Windows Defender, as Microsoft’s built-in antivirus software, offers adequate protection against viruses. Its real-time protection and robust malware detection engine provide a solid defense against various forms of malware.
However, Windows Defender should be supplemented with safe browsing habits, regular software updates, and additional security measures for a comprehensive approach to PC security.
By adopting a multifaceted strategy, users can ensure the safety of their data and identity. Remember, no single antivirus solution can guarantee absolute protection, but it serves as an essential starting point in safeguarding your PC.